[Paper Review] Explicit Occlusion Reasoning for Multi-person 3D Human Pose Estimation
Paper : https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.00090
Explicit Occlusion Reasoning for Multi-person 3D Human Pose Estimation
Occlusion poses a great threat to monocular multi-person 3D human pose estimation due to large variability in terms of the shape, appearance, and position of occluders. While existing methods try to handle occlusion with pose priors/constraints, data augme
arxiv.org
GitHub : https://github.com/qihao067/HUPOR
GitHub - qihao067/HUPOR: Explicit Occlusion Reasoning for Multi-person 3D Human Pose Estimation
Explicit Occlusion Reasoning for Multi-person 3D Human Pose Estimation - GitHub - qihao067/HUPOR: Explicit Occlusion Reasoning for Multi-person 3D Human Pose Estimation
github.com
이번에 리뷰할 논문은 ECCV 2022에서 공개될 "Explicit Occlusion Reasoning for Multi-person 3D Human Pose Estimation"라는 논문입니다. Johns Hopkins University 와 ByteDance 기업에서 연구한 논문이네요. 참고로 ByteDance는 틱톡의 모기업이며, AI Lab에서 pose와 관련된 유명한 연구들이 나오고 있네요.
우선 본 논문에서는 Pose Estimation 분야에서 난제인 Occlusion 문제를 지적하면서 기존 방법들은 pose priors / constraints, data augmentation, implicit resoning 등의 방법으로 occlusion을 처리하려고 시도하지만, 여전히 unseen pose, occlusion case, multiple people 환경에서 취약점을 보이게 됩니다. 하지만 visible cue로부터 occluded joint를 처리하는 인간의 능력에 영감을 받아 occlusion 여부에 상관 없이 bottom-up multi-person human pose estimation의 성능을 크게 향상 시키는 방법을 제안하게 됩니다.
3D Human Pose Estimation 분야에서 Occlusion 문제를 해결하기 위해 joint를 visible joint와 occluded joint로 나눠서 학습하고, occluded joint를 학습하기 위해 DSED(Deeply Supervised Encoder Distillation) 구조를 제안합니다. 또한 모델을 학습하기 위해서는 occlusion label을 생성해야하는데, 이를 위해 SSF(Skeleton-guided humanShape Fitting) 방법을 제안하여 explicitly learning이 가능하게 합니다. 실험에 의하면 SOTA를 달성한다고 합니다. 코드는 아직 공개되지 않았네요 ^^;
아래 그림은 SOTA 논문인 Smap: Single-shot multi-person absolute 3d pose estimation 의 방법과 비교한 그림 자료입니다. (이 논문을 쓸 당시의 SOTA 논문인가 봅니다.)
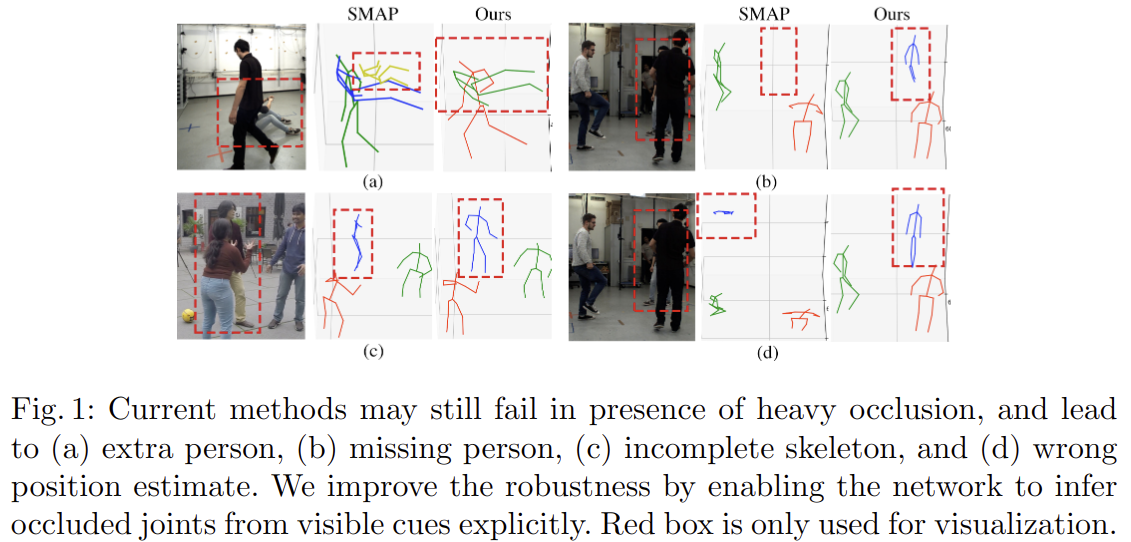
위 그림에 의하면 heavy occlusion에 의해 keypoint detection에 실패할 수 있으며 그 종류로는 extra person, missing person, imcomplete skeleton, wron position estimate를 지적하고 있습니다. 본 논문에서는 visible cue에서 joint를 estimation할 수 있도록 함으로써 robustness를 향상시킬 수 있다고 합니다.
논문의 주요 내용을 요약하면 아래와 같습니다.
- 3d human pose estimation을 방해하는 요소인 occlusion 문제를 해결하기 위해 visible keypoint detection 및 occluded keypoint reasoning 과정으로 나눠 추정
- occluded keypoint reasoning을 위해 DSED(Deeply Supervised Encoder Distillation) 네트워크 제안
- 모델을 학습하기 위해 기존 데이터세트에 pseudo occlusion label을 생성하는 SSF(Skeleton guided human shape fitting) 접근 방식을 제안하여 explicit occlusion reasoning을 가능하게 함
- 실험 결과에 의하면 occlusion 여부를 학습하면 pose estimation 결과가 향상, 또한 visible joint의 feature level 정보를 활용하면 joint를 정확하게 추론 가능
전체적인 과정은 아래와 같습니다.
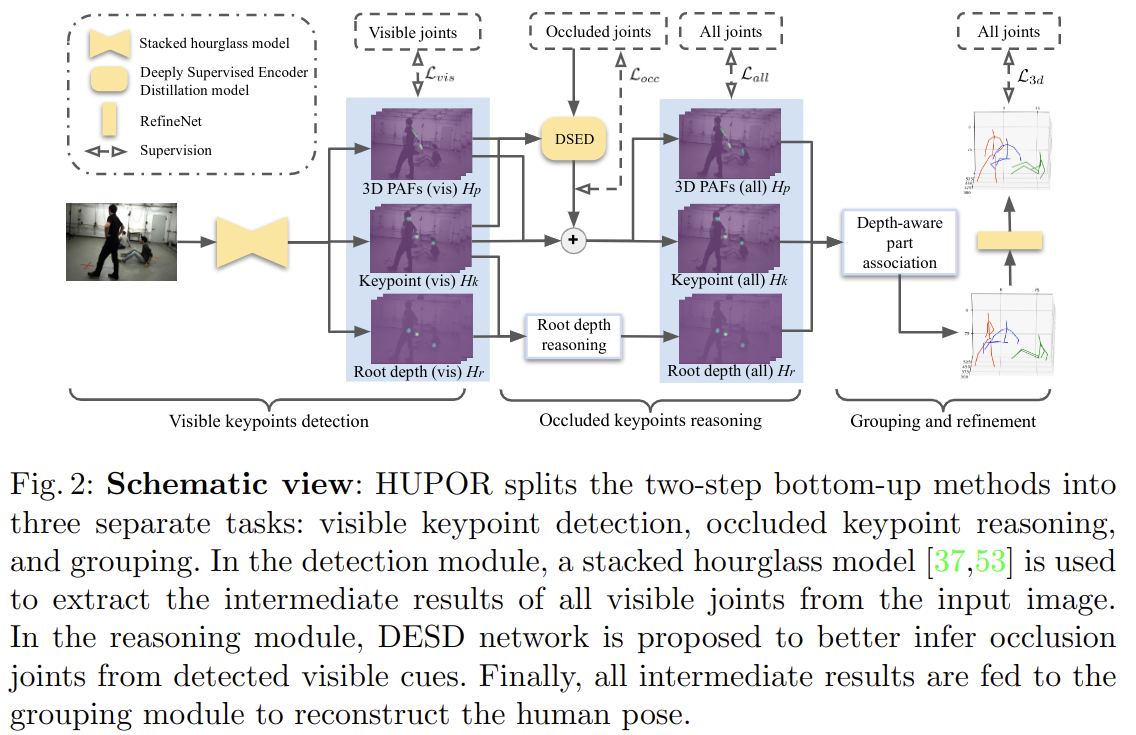
본 논문에서 제시하는 방법은 아래와 같습니다.
- visible keypoint detection을 위해 SOTA bottom-up method로 keypoint를 detection 하고, intermediate result를 기반으로 structure information을 효율적으로 학습하여 visible joint에서 occluded joint를 추론
- 그 다음 detected joint를 individual로 groping 하고, 결과를 refine 시킴. 이를 HUPOR(HUman Pose estimation via Occlusion Reasoning)이라고 함
- 이 과정에서 visible label을 얻기 위해 parametric shape models을 이미지에 fit 시킨 다음 projection relationship을 사용하여 관절이 보이는지 여부를 결정
본 논문의 Contribution은 아래와 같습니다.
- explicit occlusion reasoning에 대한 intermediate result를 사용하여 bottom-up paradigm을 발전시킴
- occluded joint를 효율적으로 추론하기 위해 DSED(Deeply Supervised Encoder Distillation) network 제안, 이는 hourglass 모델이 실패하는 것들을 해결함. 이러한 방법은 scalability 및 performance가 좋다는 것을 보여줌
- HUPOR로 표현된 3D HPE 방법은 보다 정확한 visible keypoint detection 및 occluded keypoint reasoning을 가능하게 하고, 여러 벤치마크에서 SOTA 방법을 훨씬 능가함. 그리고 wild 이미지에 잘 generalization 할 수 있음
DSED 구조는 아래와 같습니다.

특히 Occlusion label을 생성하는 과정에서는 “Cylinder Man Model” 이나 SMPL 모델을 이용하여 occlusion 여부를 판단하는 방법들은 사람과 사물에 대한 occlusion을 처리할 수 없다는 단점이 존재한다고 합니다. Cylinder Man Model은 특히 사람의 모양이 매우 거칠게 표현되고 정확도가 낮아진다고 합니다.
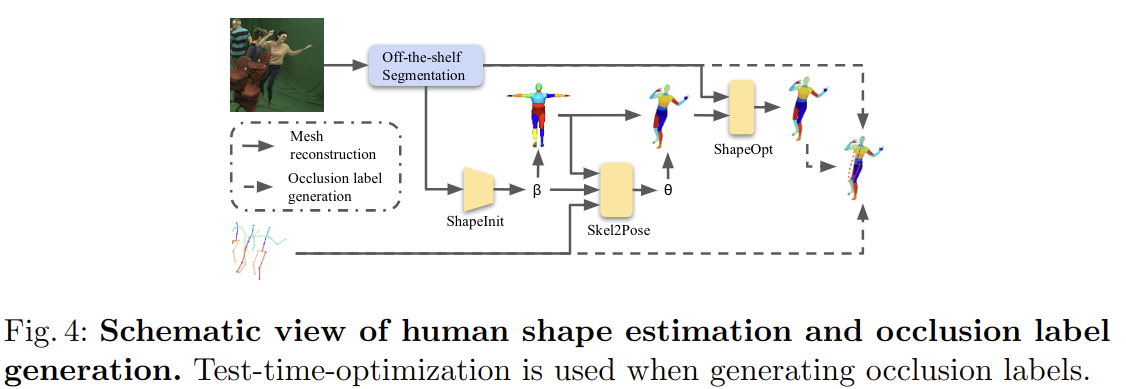
따라서 위 그림과 같이 off-the-shelf instance segmentation 모델과 SMPL 모델을 이용하여 occlusion label을 생성하는 방법을 제안하였습니다.
off-the-shelf instance segmentation 모델을 이용하여 이미지의 객체 및 사람에 대한 instance mask를 생성한 다음 각 사람에 대해 shape parameter를 학습하고, 그 다음 SMPL 모델에서 body part segmentation이 있는 human mesh를 얻습니다. 그 다음 seleton2pose 모델을 사용하여 pose parameter를 예측 한 다음, mesh로 부터 얻어진 human part segmentation label을 확인하여 joint의 occlusion label을 생성합니다. occlusion label은 0,1,2로 나타낼 수 있으며 각각 0은 truncated, 1은 occluded, 2는 visible 정보를 나타냅니다.
실험 결과는 아래와 같습니다.




