[Paper Review] Uncertainty-Aware Adaptation for Self-Supervised 3D Human Pose Estimation
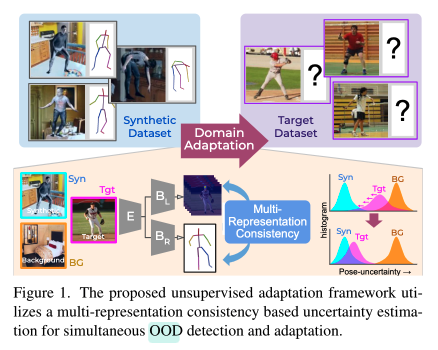
본 논문의 main contribution은 아래와 같습니다.
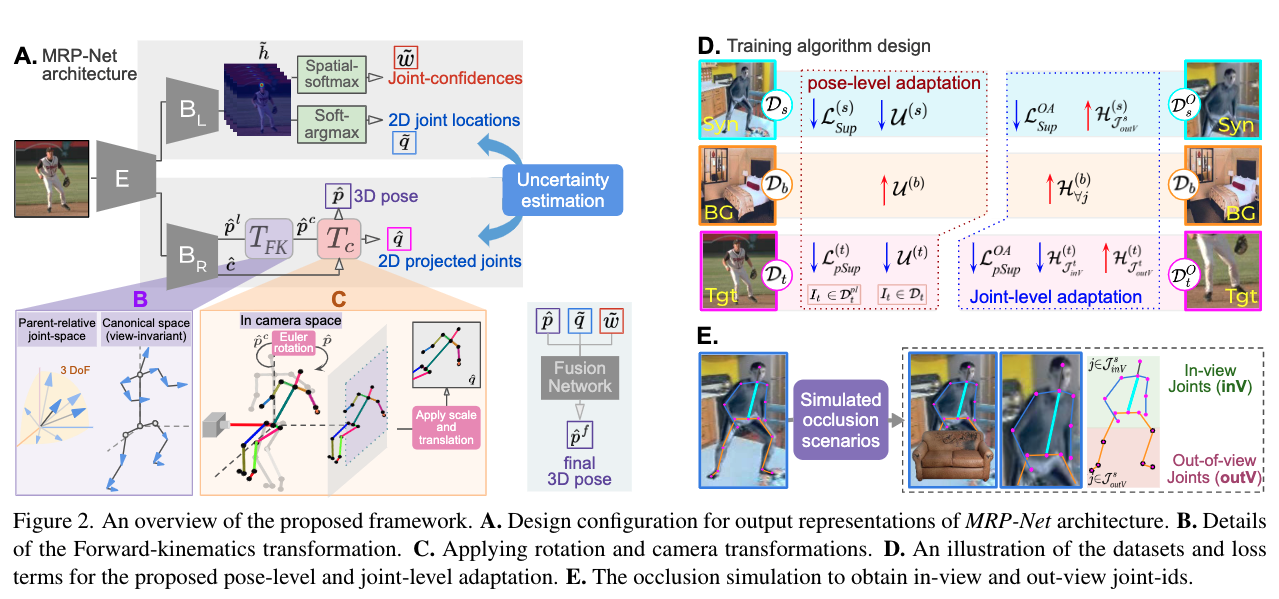
- multi-representation pose network를 사용하는 MRP-Net을 제안하였으며, pose-uncertainty는 두 가지 다양한 설계(model-free, model-based)를 기반으로 하는 2개의 output head를 통한 pose prediction간의 불일치로 정량화됩니다.
- 제안된 포즈와 joint uncertainty의 효율성을 개선하기 위해 negative sample(배경 및 시뮬레이션된 synthetic joint-level occlusions)을 사용할 것을 제안하였고, 이러한 negative를 이용하여 uncertainty estimation ability을 유지하도록 합니다.
- synthetic 데이터 세트인 SURREAL이라는 데이터는 Human3.6M에서 SOTA를 기록한 논문들의 정확도 보다 좋으며, 4개의 데이터세트에서 SOTA를 달성합니다. 또한 partial body visibility가 있는 in-the-wild sample에 대해 unsupervised adaptation에 대한 uncertainty-aware 3D pose estimation 결과를 보여줍니다.
관련 연구에서는 아래와 같이 3가지를 언급하고 있습니다.
Domain Adaptation
Doer-schet al. [17]의 방법에서는 3D human pose estimation을 위한 synthetic-to-real domain gap을 해결하기 위해 이러한 representation이 RGB image(texture and lighting variations)와 달리 domain shift의 영향을 가장 적게 받기 때문에 optical-flow 및 2D keypoints를 입력으로 사용하는 것을 제안하고 있습니다. 유사하게, Zhanget al. [97]은 depth and body segmen-tation masks와 같은 multi-modal input을 활용하는 것을 제안합니다. Muet al. [60] 방법에서는 source에서 target으로 효과적으로 적응하기 위해 several consistency loss 을 활용합니다. 본 논문에서 제안한 방법은 이러한 auxiliary input modality로 접근하지 않으며, 최근 일부 연구[77, 96]에서는 in-studio source 에서 in-the-wild target 까지 onlinetest-time adaptation of 3D human pose estimation을 제안하고 있습니다.
Pose estimation in presence of occlusion
논문에서 partial occlusion의 인간 포즈 추정 존재를 해결하는 몇 가지 방법을 찾습니다. 몇몇 작품은 추가적인 spatio-temporal 정보[13, 14, 16, 68, 73] 또는 scene related context[41, 94, 95] 방법에 기반하면서 unoccluded keypoint 조건에서 occluded keypoint의 위치를 추정하는 기술을 소개합니다. Mehtaet al. [55] 방법에서는 partial occlusion 문제를 해결하기 위해 occlusion-robust pose-maps을 사용할 것을 제안합니다.
Monocular 3D human pose estimation
논문에서는 2가지 큰 카테고리를 찾게 되는데, 첫번째는 3d pose representation을 직접 추론하는 방법이고, 두번째는 모델 기반 parametric representation을 사용하는 방법입니다. 전자의 방법은 입력 이미지를 3D pose에 직접 매핑하는 반면 후자의 방법은 미리 정의된 parametric human model의 latent parameter에 이미지를 매핑하는 방법입니다. 이러한 설정은 adversarial training을 통해 kinematic pose prior을 부여하기에 적합한 근거를 제공하게 되며, 전자의 설정은 one-stage [62, 65, 66, 80, 91, 100]와 two-stage methods [27, 53, 59, 99]로 나뉘게 됩니다. one-stage 접근 방식은 이미지를 3d pose에 직접 매핑하고, 반면 two-stage 방법은 먼저 이미지를 2d pose representation에 매핑한 다음 2d에서 3d로 lifting을 수행하기 위해 다른 매핑을 수행합니다.
Pose estimation via multi-head architecture
PoseNet3D[81]은 student-teacher multi-head framework를 사용합니다. 그러나 primary task는 fully supervised image-to-2D pose mode[61]에서 얻은 2D pose prediction에 의존하는 2D-to-3D lifting 방법이고, 이와 달리 본 논문에서는 PoseNet3D와 달리, 우리는 in-the-wild 2D pose annotation이나 temporal consistency을 활용하지 않습니다. 또한, [23, 72]방법에서는 또한 auxiliary supervision을 활용하거나 consistency loss을 통해 예측을 개선하기 위해 similarmulti-head architecture를 사용하게 됩니다. 본 논문에서는 SOTA 기술 중 어느 것도 OOD 또는 unlabeled target에 대한 self-adaptation을 위해 이러한 방법을 사용하지 않는다고 합니다.